What do you do in a seed laboratory?
The main objective of a seed laboratory is to generate detailed information about the potential performance of seeds in the field, using specialized and standardized tests to identify problems and their possible causes.
The main tests performed are:
• Purity analysis;
• Determination of other seeds by number (DOSN);
• Retention of sieves;
• Weight of a thousand seeds;
• Water content (degree of moisture);
• Tetrazolium;
• Germination;
• Accelerated aging (force).
When does seed analysis begin?
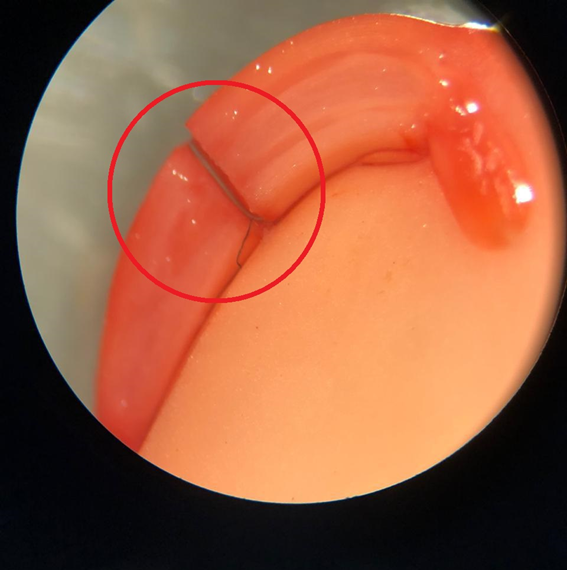
The performance of the laboratory starts immediately at pre-harvest. One of the best known analyzes is the tetrazolium analysis, carried out before harvesting, during and after harvest. Tretrazolium includes aspects such as insect damage (bed bug), moisture deterioration and detection of mechanical damage.
Example of soybean seed subjected to the tetrazolium test, showing mechanical damage directly to the embryo (causing abnormal seedlings in the germination test and low vigor):
The laboratory is part of the entire seed production chain, supported by drivers, both for seed production fields and for the formation of commercial lots during processing, assisting technical and commercial teams, until reaching the end customer.
Conclusion:
The entire process to obtain good results is due to human capital management, ensuring the importance of well-trained and qualified analysts, in addition to an infrastructure that has calibrated equipment and allows for good testing. The combination of steps makes the seed analysis and quality process a great security and transparency resource for rural producers.