Importance of inoculation in soybean
The soybean crop is one of the few cultures that, in symbiosis with a group of bacteria, of the genus Bradyrhizobium, perform the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen in a process called Biological Nitrogen Fixation (FBN). This process provides practically all the nitrogen required by the plants, generating savings for Brazilian agriculture of around 14.1 billion dollars a year.
Inoculation with Bradyrhizobium must be carried out annually, as populations of these bacteria are affected by several environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity; in addition to nutritional factors. Hence, the importance of carrying out the process successively (re-inoculation).
Soybean in rotation with rice in the floodplain, inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Photo: Luciano Cassol, Technical Consultant at 3tentos in Santa Maria/RS.
Inoculation care
When it comes to soybean inoculation, there are three important conditions that must be considered: soil, sowing and inoculant conditions. As for soil conditions, factors such as land cover have a high relationship with biological activity. The physical structure, compaction and porosity of the soil are linked to the fact that the roots need to explore the soil, as well as fertility, as microorganisms need nutrients.
The sowing conditions, mainly temperature and soil moisture, impact the inoculation efficiency. The amount of water available in the ground plays an important role in FBN, as the lack of water can negatively impact. In the case of soil temperature, temperatures above 32°C can compromise the viability of microorganisms.
Finally, the inoculant itself is a relevant factor and must be taken into account, especially aspects related to origin, quality, concentration and registration. In addition to these, other points of attention also stand out: time between inoculation and planting; pesticides used in seed treatment and application quality.

Example of an area using quality inoculants.
Source: Sabrina Dahmer, APD Santa Bárbara do Sul.
Inoculation is essential to improve the exploration of the productive potential of cultivars, and may be responsible for an average increase of 8% in productivity.
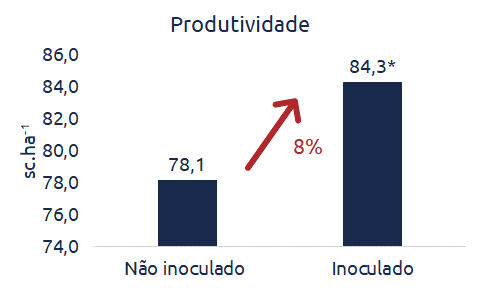
Data: CETEC, 2020/21 harvest. *Compiled from inoculation treatments performed in controlled research environments.
Thus, inoculation is as essential as the use of fertilizers, generating an increase in productivity and making the soil more biologically active. Hope the information has helped! If you have any questions, please contact the 3tentos Technical Consultants team or contact the Research, Development and Innovation Department (PDI)!!